Connection Types: NPT (National Pipe Tapered)
What are NPT Fittings?
NPT connections seal pipes for fluid and gas transfer. They’re available in iron and brass for low-pressure applications and carbon and stainless steel for higher pressure. The nominal pipe size can be identified by physically measuring the thread diameter, then subtracting 1/4″. NPT (or National Pipe Taper) is a U.S. standard for tapered threads widely used on pipes and fittings for over 100 years.
NPT connections rely on thread deformation- a metal to metal sealing design where the threads of the connectors themselves form together. This design is ideal fore single assembly applications and not recommended where connections will be assembled and disassembled frequently due to wear on the threads from deformation.
Disadvantages of Using NPT Fittings:
- Can be prone to port expansion or cracking from over tightening
- Can make it more difficult to properly orient shaped connectors
- Thread lubricant required can cause system contamination
- Are not suitable for the highest pressures
Sealing performance decreases rapidly with re-assembly and larger sizes are more prone to leaking because of the leak path size
Advantages of Using NPT Fittings:
- Are readily available
- Come in a large variety of sizes, shapes, combinations and materials
- Widely used and well known
- Offer simple assembly without flaring of tubes, using sleeves, or introducing seals or o-rings
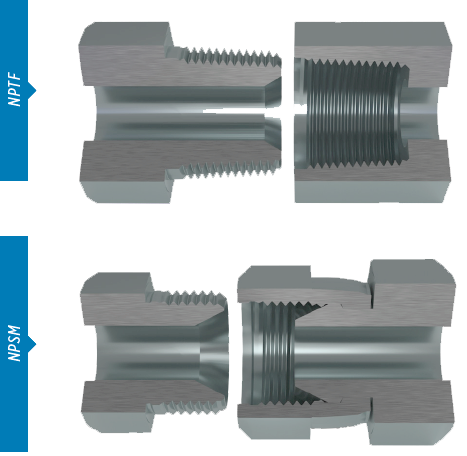
NPTF and NPSM Thread Styles
Two of the most common variations of this pipe thread standard are NPTF and NPSM thread styles.
Where traditional NPT threads have a small clearance between the crest and root of the mating threads requiring the use of sealant, the NPTF thread root does not allow this clearance. It contacts and deforms the mating thread crest. NPTF, or National Pipe Taper Fuel, style connections are widely used in fluid power systems. This type of connector is designed to provide a dry thread seal. However, lubricant is often still used to ease assembly.
NPSM, or National Pipe Straight Mechanical threads, are also often found in fluid power systems. The female component incorporates a straight, non-tapered thread with an inverted 30° chamfer of the male connector on the seat of the female. This is a mechanical seal. If and NPTF male is properly chamfered it will also seat with NPSM female connection. They are especially suited for manufacturers and end users that rely on versatility.
NPT style threads are very similar to BSP, certain DIN styles, and other non-US thread styles. Although visually very similar, the differences in thread dimensions, pitch and angle make them incompatible, so care needs to be taken to properly identify your connection to create a safe and leak resistant seal.